What Is The Likely Makeup Of The Buying Center? Who Plays Or Has Played Which Roles
Creating Products and Pricing Strategies to Meet Customers' Needs
94 Buyer Behavior
- How do consumers and organizations make buying decisions?
An organisation that wants to be successful must consider buyer beliefs when developing the marketing mix. Buyer behavior is the deportment people take with regard to buying and using products. Marketers must understand buyer behavior, such as how raising or lowering a cost will touch the heir-apparent's perception of the product and therefore create a fluctuation in sales, or how a specific review on social media tin create an entirely new direction for the marketing mix based on the comments (heir-apparent behavior/input) of the target market place.
To empathize buyer beliefs, marketers must sympathise how customers make buying decisions. Consumers and businesses have processes for making decisions almost purchases. These decision-making processes are afflicted by cultural, social, private, and psychological factors. The consumer decision-making process has several steps, which are shown in (Figure).
Consumer Purchase Controlling Process
(Attribution: Copyright Rice Academy, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license.)
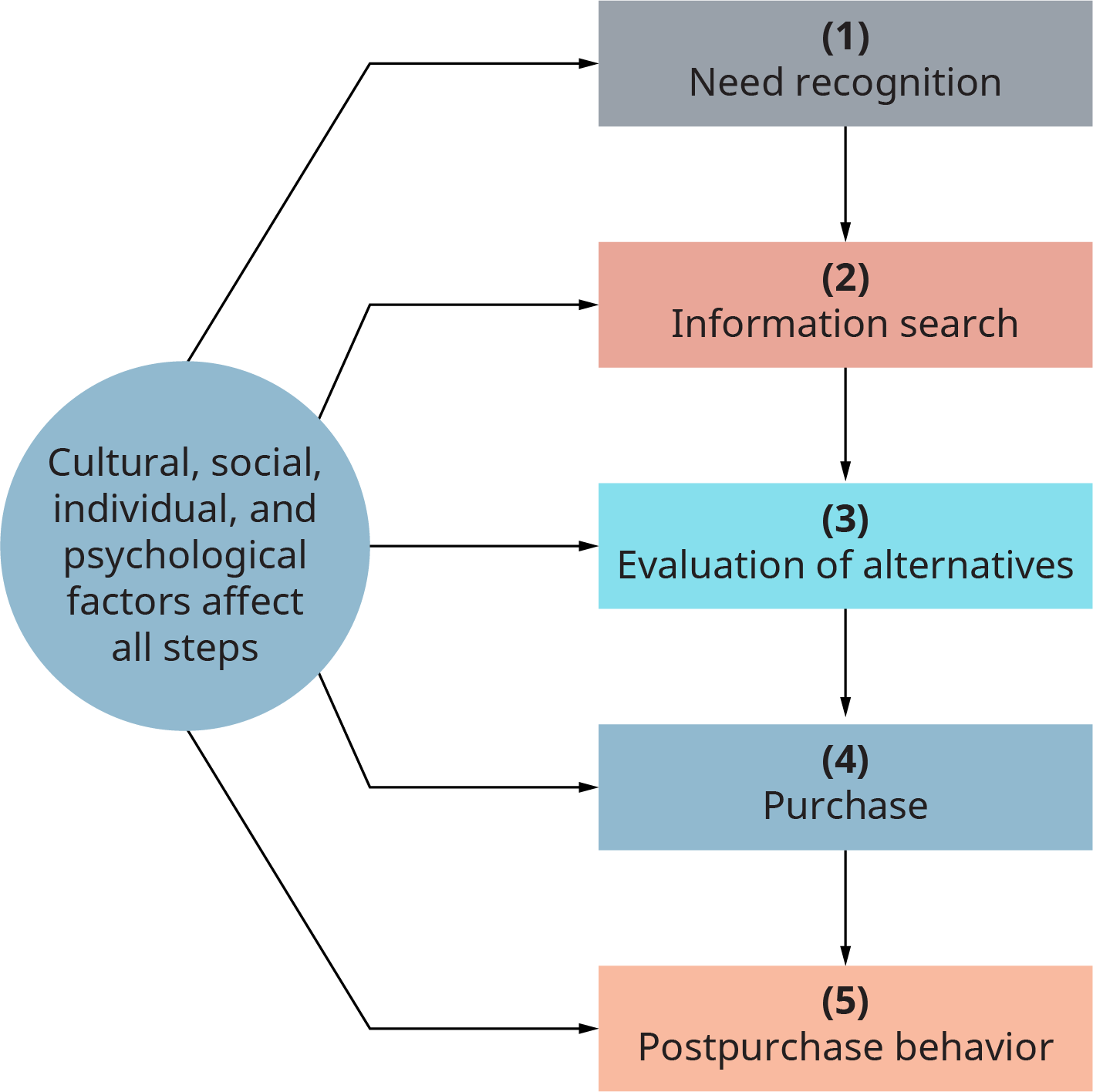
The process starts with need recognition. Need recognition could be as simple as running out of coffee. Need recognition could also take place over several months, such as when repeated car repairs influence a consumer to make a decision to buy a new auto. (Pace 1 in (Effigy)).
Side by side, the buyer gathers information. If the consumer is making a decision to buy a house, he or she might research data nearly financing, available homes, styles, locations, and so along (Step 2). Once the consumer has gathered the information, he or she must evaluate alternatives (Step 3). For instance, a consumer might eliminate all homes that cost over $150,000 or are more than than a 30-minute drive to work. After evaluating the alternatives, the consumer will make a decision based on those alternatives. So the consumer makes the purchase decision, the determination to buy or not to buy (Step iv). Finally, the consumer assesses the decision itself and his or her satisfaction with the purchase, which would include not only the abode, but the buying feel as well (Step 5).
Influences on Consumer Decision-making
Cultural, social, individual, and psychological factors have an impact on consumer decision-making from the time a person recognizes a need through post-purchase behavior. We will examine each of these factors in more detail. It is important to understand the relevance of these influences on consumer decision-making.
Civilisation
Purchase roles within the family are influenced by culture. Civilization is the set of values, ideas, attitudes, and symbols created to shape human behavior. Culture is the function of customs and traditions of a group of people that is transformed into its art, food, costumes/clothing, architecture, and linguistic communication, every bit well every bit other unique manifestations of a specific grouping of related individuals. Culture is environmentally oriented. For case, the nomads of Finland take adult a culture for Arctic survival. Similarly, the natives of the Brazilian jungle have created a culture suitable for jungle living.
Culture by definition is social in nature. It is human interaction that creates values and prescribes acceptable beliefs. Civilisation gives gild to society by creating common expectations. Sometimes these expectations are codified into law; for example, if y'all come to a red light, you stop the machine. In some cultures, a young man undergoes a special rite of passage from youth into adulthood (such as a bar mitzvah in Jewish culture). In other cultures, young women accept a rite of passage just immature men do not (such equally a quinceañera in Hispanic culture). As long equally a value or conventionalities meets the needs of club, it will remain role of the civilization. If it is no longer functional, the value or belief fades abroad. For instance, the value that very large families are "skilful" is no longer held by a majority of Americans. This is because most Americans alive in an urban rather than a rural surround, and children are no longer needed to perform subcontract chores.
Social Factors
Nigh consumers are likely to seek out the opinions of others to reduce their search and evaluation effort or doubtfulness, especially as the perceived gamble of the determination increases. Consumers may as well seek out others' opinions for guidance on new products or services, products with image-related attributes, or products where attribute information is lacking or uninformative. Specifically, consumers interact socially with reference groups, stance leaders, and family members to obtain production information and decision approval. All the formal and breezy groups that influence the buying behavior of an individual are considered that person's reference groups. Consumers may use products or brands to identify with or get a member of a group. They learn from observing how members of their reference groups consume, and they use the aforementioned criteria to make their own consumer decisions. A reference group might be a fraternity or sorority, a group y'all work with, or a guild to which you lot belong.
Private Influences
A person'southward ownership decisions are also influenced by personal characteristics unique to each individual, such equally gender and personality. Individual characteristics are more often than not stable over the form of one's life. For instance, most people do non alter their gender, and the act of changing personality requires a complete reorientation of one's life.
Physiological differences between men and women result in different needs, such as health and dazzler products. Simply equally of import are the distinct cultural, social, and economical roles played by men and women and the effects that these accept on their decision-making processes. Men and women also shop differently. Studies prove that men and women share similar motivations in terms of where to shop—that is, seeking reasonable prices, merchandise quality, and a friendly, low-pressure environment—but they don't necessarily feel the aforementioned virtually shopping in full general. Nigh women enjoy shopping; their male counterparts claim to dislike the experience and shop only out of necessity. Furthermore, men desire simple shopping experiences, stores with less variety, and convenience. When it comes to online shopping, gender differences go on. According to recent research, women tend to shop based on their future needs, while men tend to shop when their demand is firsthand. In add-on, women tend to brand impulse buys more often than men, who tend to call up logically when making purchase decisions.
Catalin Zorzini, "Infographic: An Analysis of Online Shopping Habits of Men & Women," https://ecommerce-platforms.com, accessed October eight, 2017.
Each consumer has a unique personality. Personality is a wide concept that tin can be thought of as a way of organizing and grouping how an individual typically reacts to situations. Thus, personality combines psychological makeup and environmental forces. It includes people's underlying dispositions, especially their most dominant characteristics. Although personality is one of the to the lowest degree useful concepts in the study of consumer behavior, some marketers believe that personality influences the types and brands of products purchased. For instance, the blazon of car, clothes, or jewelry a consumer buys may reflect ane or more personality traits.
Psychological Influences
An private'southward buying decisions are further influenced by psychological factors such as perception, beliefs, and attitudes. These factors are what consumers use to interact with their world. They are the tools consumers utilise to recognize their feelings, gather and analyze information, formulate thoughts and opinions, and take action. Unlike the other 3 influences on consumer behavior, psychological influences tin can be affected by a person's environment considering they are practical on specific occasions. For example, individuals volition perceive different stimuli and process these stimuli in different ways depending on whether the individual is sitting in class concentrating on an instructor'south lecture, sitting outside of grade talking to friends, or sitting at abode watching goggle box.
B2B Buy Controlling
Business concern-to-business (B2B) buyer behavior and business concern markets are different from consumer markets. Concern markets include institutions such as hospitals and schools, manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers, and various branches of authorities. The key difference between a consumer production and a business organisation product is the intended use. For example, if a consumer purchases a certain brand of computer for use at home, it is considered a consumer good. If a purchasing agent for Netflix buys exactly the same reckoner for Netflix scriptwriter, it is considered a business skilful. Why? The reason is that Netflix is a business, and then the estimator will exist used in a business surround.
The Decision-Making Process
The purchases that organizations make often involve greater take chances than purchases fabricated past private consumers. For this reason, businesses (and other organizations) tend to base purchase decisions on more information and brand purchase decisions based on rational decision-making so purchases will optimize value for the organization and minimize gamble. For this reason, the business buy decision-making process differs from the consumer process. The steps are similar: demand recognition, setting specifications, data search (including identification of suppliers), evaluation (including evaluation of suppliers), purchase ("become or no-go"), and post-buy evaluation. The major difference betwixt the two processes is that businesses decide beforehand what exactly is needed on the purchase (setting specifications) and then seek information regarding products that see those specifications. In this way, the purchases are more likely to satisfy the needs of the overall organization, thus reducing the adventure.
Characteristics of the B2B Market
The main differences between consumer markets and business markets include the following:
- Purchase volume: Business customers buy in much larger quantities than consumers. Mars must purchase many truckloads of carbohydrate to brand one day's output of Grand&Ms. Home Depot buys thousands of batteries each day for resale to consumers. The federal government must utilize (and buy) millions of pens each solar day.
- Number of customers: Business organisation marketers usually have far fewer customers than consumer marketers. As a result, information technology is much easier to place prospective buyers and monitor electric current needs. For case, there are far fewer customers for airplanes or industrial crane companies than in that location are for consumer appurtenances companies since there are more 125 million consumer households in the U.s..
- Location of buyers: Business customers tend to be much more geographically concentrated than consumers. The computer industry is concentrated in Silicon Valley and a few other areas. Aircraft manufacturing is establish in Seattle, Washington; St. Louis, Missouri; and Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas. Suppliers to these manufacturers oftentimes locate shut to the manufacturers to lower distribution costs and facilitate advice.
- Direct distribution: Business sales tend to be made direct to the buyer because such sales frequently involve large quantities or custom-made items such equally heavy machinery. Consumer appurtenances are more probable to be sold through intermediaries such as wholesalers and retailers.
- Explain the consumer purchase controlling procedure.
- Explain the differences between the concern purchase decision-making procedure and the consumer buy decision-making process.
- How practise business concern markets differ from consumer markets?
Summary of Learning Outcomes
- How practice consumers and organizations make buying decisions?
Buyer behavior is what consumers and businesses do in social club to buy and utilize products. The consumer purchase decision-making procedure consists of the post-obit steps: recognizing a demand, seeking data, evaluating alternatives, purchasing the product, judging the purchase outcome, and engaging in post-purchase behavior. A number of factors influence the process. Cultural, social, individual, and psychological factors have an affect on consumer determination-making. The business buy decision-making model includes the following steps: need recognition, setting specifications, data search, evaluation of alternatives against specifications, purchase, and post-purchase beliefs. The main differences between consumer and business organisation markets are purchase volume, number of customers, location of buyers, straight distribution, and rational buy decisions. Companies learn more about their target markets by conducting marketing research—the process of planning, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to a marketing decision.
Glossary
- buyer behavior
- The deportment people take in buying and using appurtenances and services.
- culture
- The set up of values, ideas, attitudes, and other symbols created to shape human behavior.
- personality
- A manner of organizing and grouping how an individual reacts to situations.
- reference groups
- Formal and breezy groups that influence buyer beliefs.
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/businessopenstax/chapter/buyer-behavior/
Posted by: hayesbegfring.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Likely Makeup Of The Buying Center? Who Plays Or Has Played Which Roles"
Post a Comment